
As a link builder or marketer, there are certain types of unnatural links that you should completely avoid in your link-building strategy.
Toxic links, as we’ve explained previously, alert Google that you’re using spammy link-building tactics to improve your ranking on search result pages. These are the links you want to steer clear of.
One type of toxic link is an unnatural link. These are links that have no contextual relevancy and offer no value to the user. Instead, they’re simply spammy attempts at improving a site’s SEO rankings.
As we will explain shortly, unnatural links are either links on your own website that send users to irrelevant sites, or they are links on other sites that direct to yours.
The main issue with unnatural links is that Google can penalize you for having them on your website or on another site that directs to yours.
Key Points
Unnatural links are a form of toxic link that can either exist on your own website or that can be found on an external website that links to yours.
Google can impose penalties on websites that use unnatural links to manipulate PageRank (PR).
An unnatural links penalty can lead to a significant decrease in organic search traffic to your website.
If you have been penalized by Google for unnatural links, there are certain steps you can take to have the penalty lifted.
How Does Google Manage Toxic Links?
Despite Google's claims to the contrary, recent evidence shows that toxic links are indeed a factor in their ranking algorithms.
Information gleaned from Google’s documentation leak includes mention of “BadBackLinks.” This means that a page can be penalized for having poor-quality backlinks, and proves that Google does recognize the impact of undesirable links.
What Is an Unnatural Link?
What makes a link unnatural is that there’s no obvious reason that the link placed in the content should direct users to that particular site.
Unnatural links often stick out like a sore thumb because there's no natural flow or context for their inclusion.
Picture a digital marketing agency's website suddenly linking to a corporate bank with no business relationship or relevance to motivate it. This type of link is considered unnatural.
This is in contrast to natural backlinks, which are earned organically over time as people find and link to your content.
For example, if your digital marketing agency collaborates with the corporate bank or is known for working with financial clients, including a link to their site while discussing their marketing campaigns would make sense.
This creates a relevant and valuable connection for the user.
Unnatural links are bad links. Here’s why:
Misleading: They add no value for the user and create confusion about the relevance or credibility of the linked content.
Manipulative: These links are often used to artificially boost search engine rankings. This tactic goes against search engine guidelines.
Potential penalties: Search engines like Google use sophisticated algorithms to spot and penalize websites engaging in such practices. This can lead to a drop in rankings or even removal from search results.
Unnatural links are also referred to as harmful or spammy links.
This is because they are often built by spammers or purchased through tactics like link schemes.
What Is a Link Scheme? 💡
A link scheme is a link-building tactic that is intended to manipulate rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). This violates Google's Spam Policies, which explicitly prohibit practices that deceive or manipulate search engines for better ranking. More on this later.
Why are unnatural links bad?
Unnatural links are bad because they:
Impact the integrity of Google’s SERPs, and the search engine may manually penalize websites.
Are often purchased or built by spammers and, therefore, aren’t a true reflection of the website’s SEO performance.
Attempt to deceive Google into thinking your website has a high domain authority (DA) when it actually doesn’t.
Give your website an unfair advantage over others that don’t engage in black-hat SEO practices, such as paying for links.
Are vulnerable to updates and only provide short-term benefits, which mean that websites with unnatural links are more likely to eventually suffer ranking losses, especially with updates to the sites or content they link to.
What Is Black Hat SEO? 👈
Black hat SEO is using unethical tactics to get a website to rank higher in the search results. These techniques include keyword stuffing and using private link networks.
What Is a Google Penalty?
A Google penalty—also called a manual action—is a measure Google takes when a website violates the guidelines set out in Google Search Essentials.
When a website violates Google’s guidelines and incurs a penalty, it will experience a drop in search rankings or, in extreme cases, be removed from Google’s search index altogether.
Penalties can be applied manually by Google's webspam team or by Google's search algorithms.
As we mentioned earlier, Google’s documentation leak revealed that the search engine does recognize bad or irrelevant links—but it’s also sophisticated enough to ignore certain instances thereof.
However, if you consistently build bad backlinks and Google suspects that you’re attempting to manipulate search results, you may receive a penalty.
How do unnatural link penalties occur?
One of the most common backlink activities penalized by Google is unnatural outbound links.
A violation of Google’s guidelines is usually the result of using black-hat SEO tactics and having unnatural and toxic links in your website’s backlink profile.
This penalty would come from Google’s spam team in the form of a manual action, which is a restrictive measure.
You'll know if you have had a manual action issued against your website when you see a message like this on your Google Search Console:
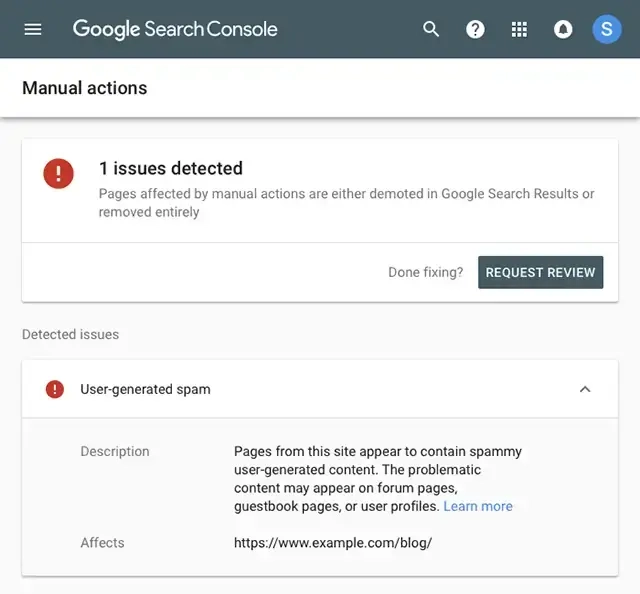
Google Search Essentials guidelines
According to Google, you can receive a manual action or penalty for “a pattern of unnatural, artificial, deceptive, or manipulative links pointing to pages.”
Additionally, Google Search Essentials states that any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme and are in violation of their guidelines.
This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.
What happens when you receive an unnatural links penalty?
The result of receiving a Google penalty is an almost immediate decline in organic search traffic.
The good news is that your website can recover from a Google penalty and you can return to your previous ranking positions. We’ll discuss how you can achieve this shortly.
What Happens to Your Website If Google Penalizes You
The first thing that is likely to happen should Google impose a manual action, is that your site’s rankings will be negatively affected.
However, an indication of a penalty can sometimes be less obvious.
Here’s what to look out for:
You may no longer rank at all for something you used to rank well for.
Your web traffic reduces month by month.
You might suddenly disappear from search rankings for valuable keywords associated with your content.
Any new content seems to struggle to get into Google’s index.
How do you get Unnatural Links
Often, the cause of unnatural links is simply having an inexperienced SEO specialist work on your link building strategy or having a low-quality business build your backlinks.
A classic example of this is indiscriminately buying backlinks from freelancers on crowd-sourcing sites like Fiverr. Don't go that route!

Unnatural links can be purchased and are typically created by scrapers and spammers, or they can be the result of a negative SEO attack from a competitor.
What Is a Negative SEO Attack? 💻
A negative SEO attack is when a black-hat SEO link points toxic backlinks to another website. Usually carried out by spammers, the intention behind it is for Google to see the links and then penalize the website in question. The result? A significant hit to your search engine rankings.
Examples of Unnatural Links
There are several types of unnatural links. This is not an exhaustive list, but these are some common examples that could result in a Google penalty.
Link schemes
Also known as link farms or private blog networks (PBNs), link schemes are a link building tactic that involves someone dedicating a website to the sole purpose of building links.
PBNs are connected sites that link to each other to gain SEO benefits. PBN links usually aren’t of any value to users and, as a result, can be penalized by Google.
Here is an example of an obvious PBN:
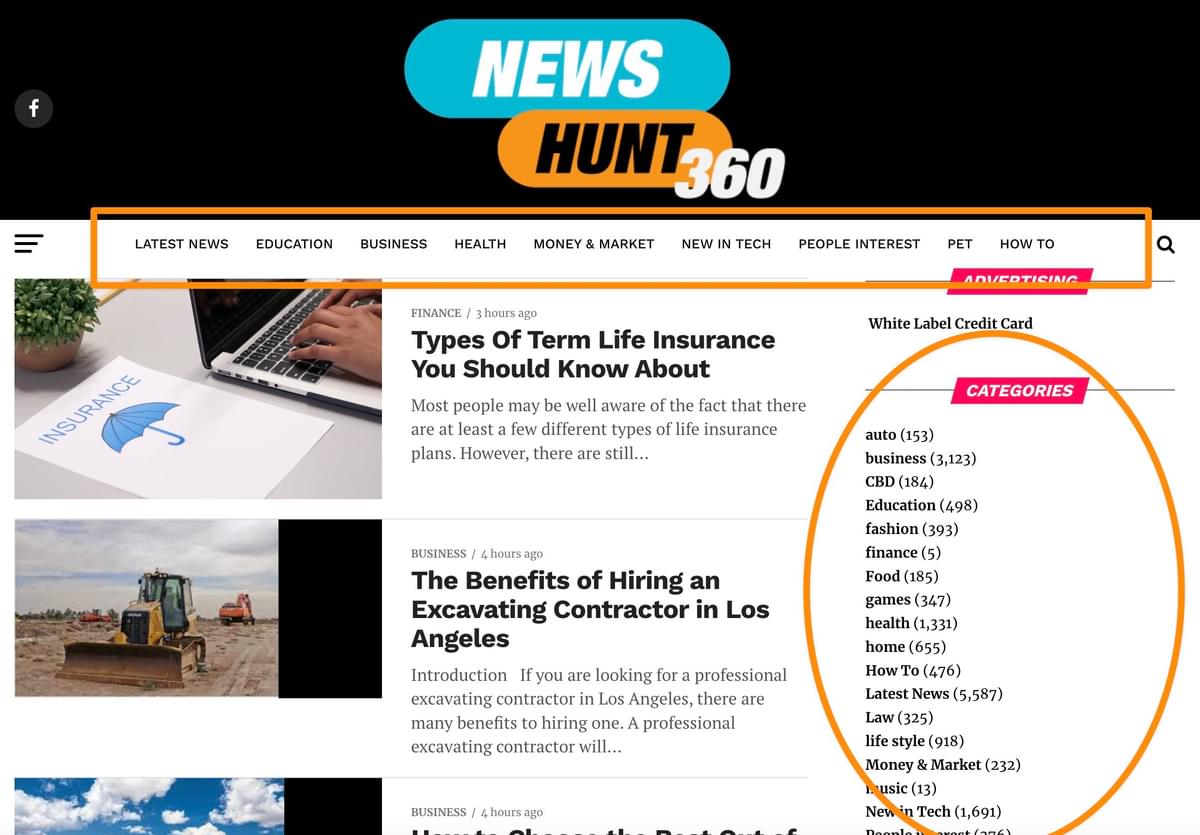
The tell-tale signs
The example above features some very obvious indicators:
An obscene number of random categories—literally every category imaginable!
This tells us they're trying to sell links to every man and his dog.
Extremely generic content titles.
Generic stock images.
If you peek behind the scenes, this site ranks for ZERO valuable keywords.
The most terrifying thing is that this site is publishing multiple posts per day, which means people are actually paying for this rubbish!
This is one of the first types of unnatural links that Google has been penalizing since the start of SEO. This is because these links are not contextually relevant and they don’t provide value. They also give websites an unfair advantage when it comes to a site’s ranking.
Low-quality web directories and bookmarking sites
Having your backlink listed on bookmarking sites and web directories can be beneficial to your link building strategy.
However, when your backlink is listed on low-quality and spammy sites that don’t provide any value to users, you’ve found yourself a quick way to rack up unnatural links.
Take a look at this example of a low-quality, spammy web directory:

Injected links
Possibly, one of the quickest ways to incur a Google penalty is through injected links.
Injected links happen when automated software and scripts are used to inject links into a website. This is often done by hackers who exploit vulnerabilities in the website's code or content management system.
Here’s how you can spot them:
Injected links can be added through various methods, including exploiting site vulnerabilities, injecting malicious code into a website, or hackers adding malicious SQL statements into an entry field.
Injected links are used to artificially boost the search engine rankings of the attacker's site by creating backlinks from other websites.
They pose a major threat to your website’s security and reputation, and your website may need to be restored from an older version.
Sitewide links
These are links that appear on every page of the website. They are most often found in the footer, header, or navigation menu.
Sitewide links are often placed there by a website developer or designer. These links are okay and won't be flagged by Google if they're natural.
At LinkBuilder, we make use of sitewide links in our header:
These won’t be flagged by Google because they’re natural and provide quick and easy access to essential pages.
However, some companies actually pay for sitewide links on other websites, which is a big no-no. These links are misleading and erode trust with both users and search engines.
Press release and syndicated content
Generally speaking, press releases and syndicated content are fine, provided that you use branded anchor texts within them.
However, many people still try to use keyword stuffing to bolster their rankings.
Keyword stuffing refers to using a keyword or keywords so many times in a press release or syndicated content that it becomes inorganic (or unnatural). Often, keywords are repeated so frequently that the press release seems artificial and makes little to no sense.
The best practice is to write press releases that provide genuine value to users without aiming for search engine gains.
Blog comments
A couple of years ago, link building in blog comments was a commonplace strategy.
However, this inadvertently led to comment sections being misused by spammers who over-optimize them with keywords and backlinks to manipulate PageRank:
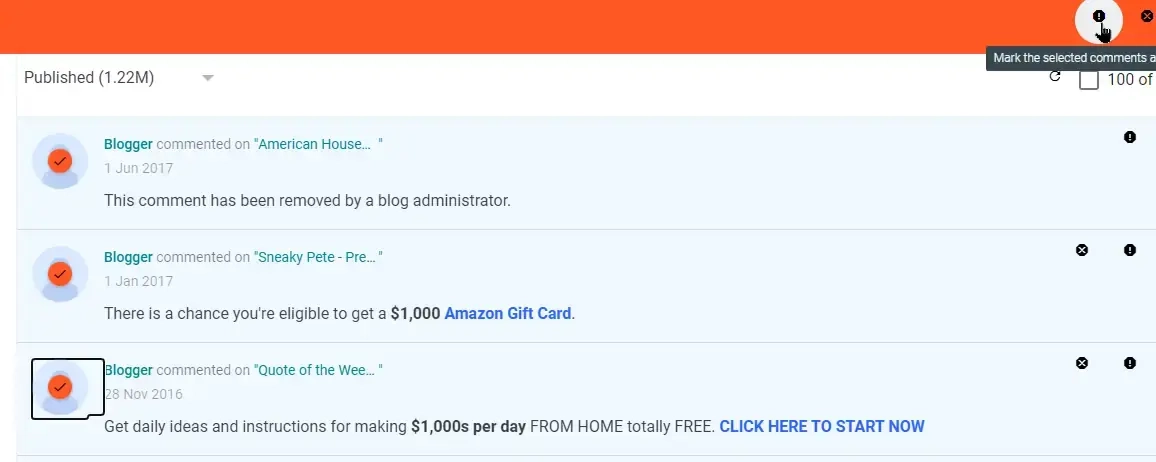
These links don’t offer any value to users and Google almost always ignores them.
Forums
While forums are a great way to boost your brand awareness, forum backlinks are often spammy and include plenty of instances of keyword stuffing in bios, profiles, and signatures.
Often, user profiles are created that never post anything—they only use the backlink field and then go on to stuff the bio with keywords.
This is sometimes referred to as user-generated spam.
Here are two examples of forum link spam:
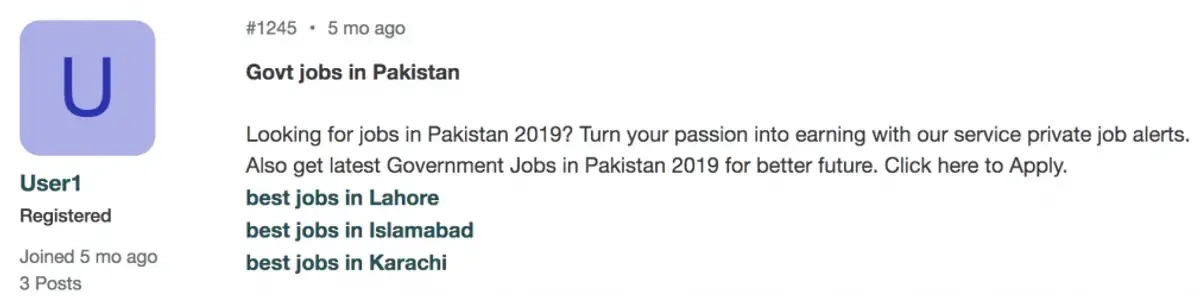
Typically, these bios, profiles, and automated posts go unread as users quickly realize they aren’t relevant and provide no real value.
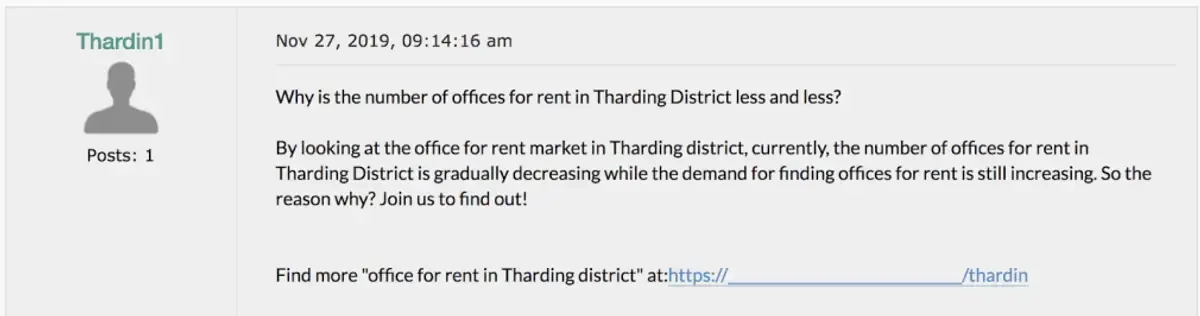
Redirected domains
You can easily trigger a manual action penalty for unnatural links by having an old domain that redirects to a new domain.
This is an extremely common form of unnatural links nowadays. People buy expired domains with solid link profiles, and redirect them to their current domains.
Google has become pretty savvy in detecting this method now, and you will very rarely get any benefit from these kinds of links.
Google’s Rules for Unnatural Links
In order to avoid running into issues with unnatural links penalties from Google, it’s a good idea to understand exactly how the search engine treats these links. These insights should help you when building links.
A single unnatural link won’t lead to a Google penalty. A manual action is usually only triggered by two to three (or more) manipulative links.
A link’s lifespan won’t stop a manual action. It doesn’t matter whether your unnatural link was built five years ago or five days ago, Google won’t view them differently.
Your whole website will be affected: Google doesn’t only penalize certain pages or sections of your website where unnatural links are hosted. Instead, it’s more likely that your website will be penalized in totality. So, you won’t be losing traffic to a single page, you’ll lose traffic to your entire site.
Google WILL spot money anchors. Google is exceptionally good at picking up money anchors, which are links that use exact-match anchor text for keywords that a website is trying to rank for. Using too many exact-match anchor texts can negatively impact your site's ranking because Google favors a natural and diverse link profile.
Will Authority Save You from a Google Penalty?
Previously, experts believed that Google didn’t judge certain sources of unnatural links more favorably simply because they were more authoritative.
The thinking was that as long as a link was manipulative and unnatural, that’s all that Google needed to penalize you.
However, the Google data leak revealed that the search engine does have an internal sitewide authority score rating. This means it does consider the trustworthiness of websites in this regard.
Receiving an unnatural link from one of these trusted websites is likely to be ignored at worst. The real problem surfaces when you have a high volume of unnatural links from less authoritative or low-quality websites.
Here is an example of a manual action. You can see that Google didn’t identify the unnatural links they detected.
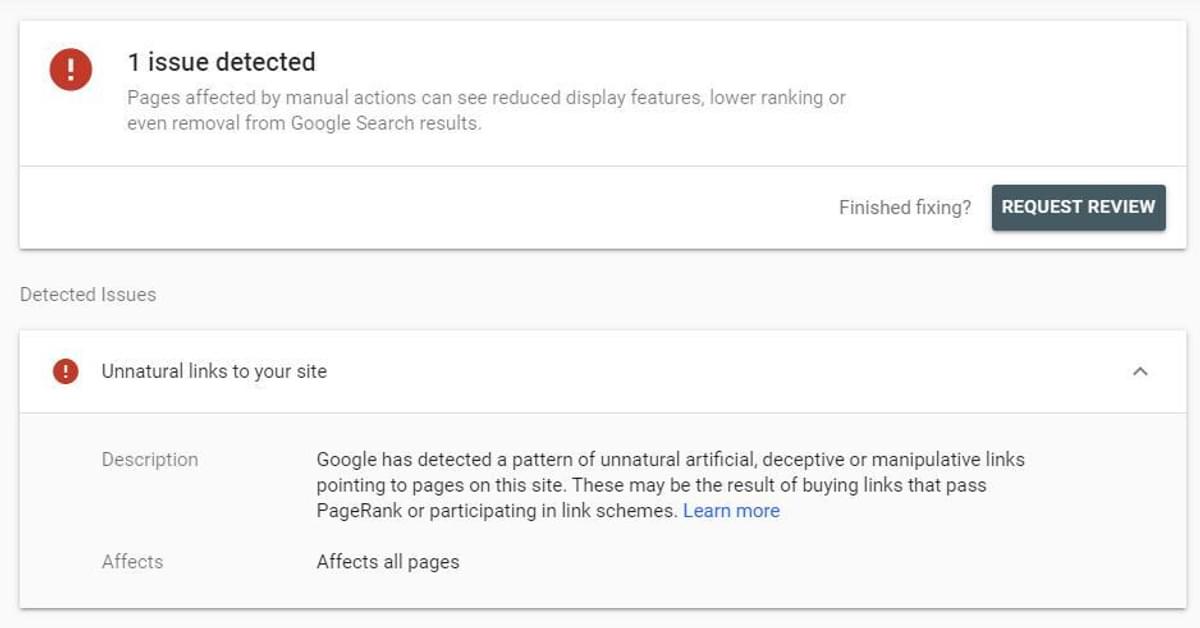
This leaves webmasters with a massive task on their hands. They have to identify and act on any and all unnatural inbound and outbound links, which is a significant undertaking.
What to Do If You Get an Unnatural Links Penalty
If a manual action was issued against your website for unnatural links, we’ve put together this step-by-step guide to follow before you approach Google with a reconsideration request.
1. Identify potentially harmful links
Firstly, you can use tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or Majestic to identify unnatural outbound or inbound links.
Here is an example of what Semrush’s dashboard looks like when you run a backlink audit on the platform:
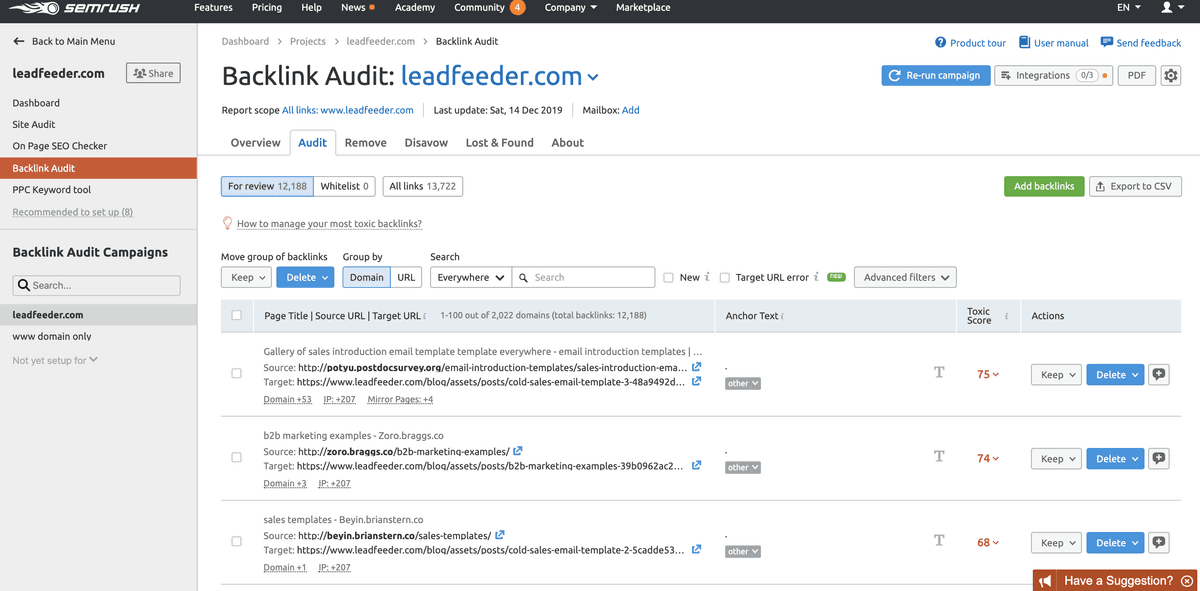
Your next step is to export the list of backlinks into an Excel or Google Sheets spreadsheet. Then you can sort your backlinks based on their toxicity score. Links with a score of 60 or higher should take priority.
2. Do a manual review
Go to each site where your data has indicated an unnatural link may exist and manually review the website. Look out for any of the examples of unnatural links that we mentioned above and see whether you can pick up any patterns in the URLs.
If you do detect a pattern of any sort within the URLs, it’s likely that you have link spam coming your way.
3. Take action
You can now divide your list into sections based on the action you want to take for each link. This could include adding the link to your disavow list, flagging it for further review, or leaving it as is.
What does it mean to disavow a link? 🤔
The definition of disavowing within the SEO context means to get rid of any harmful links that point to your website with Google’s Disavow Tool.
You can take this action when you can’t reach out to a website owner to remove an unnatural link that directs to your website. You would essentially be asking Google not to consider these links when assessing your website.
4. Remove harmful links
Now that you have your disavow list ready, you can create a disavow file and upload it to Google Search Console. It would also be advisable at this point to add an annotation to your Google Analytics so you can monitor any fluctuations in your traffic.
👉 See our guide on how to disavow backlinks
This is a significantly time-consuming process. However, it is essential for webmasters and link builders to go through these steps before submitting a request to Google to review a manual action.
You should request that a link be set to a nofollow status if they are a result of:
A paid link.
A press release.
User-generated spam.
Third-party widget links.
A sitewide link.
If you have tried contacting the website’s administrator and they won’t respond to your nofollow request, it’s best to disavow the link.
You should attempt to remove links that are listed on web directories or bookmarking sites.
If there is absolutely no way to have these links removed, they should be added to your disavow list.
You can then go to each site where your data has indicated an unnatural link may exist and manually review the website. Look for any of the examples of unnatural links that we mentioned above and see if you can pick up any patterns in the URLs.
If you do detect a pattern of any sort within the URLs, it’s likely that you have link spam coming your way.
You can now split your list up into sections based on the action you want to take for each link. This could include adding the link to your disavow list, adding it to a further review list, or leaving it as is.
How to Get Google to Reconsider Your Penalty
A reconsideration request is a process where webmasters can ask Google to review their site after addressing issues that led to a manual penalty. Unfortunately, it’s a long journey.
Google is not likely to budge on your first reconsideration request. In fact, it often takes two to three requests before seeing any positive results.
This means you need to be prepared for a process that can take around six months or even longer.
Before submitting a reconsideration request, you’ll need to fix the issues that led to the penalty. This includes removing or disavowing unnatural backlinks and ensuring your site complies with Google's guidelines.
When you’re ready to submit, log in to your account to access Google Search Console and choose the website affected by the penalty.
From the sidebar, select 'Security & Manual Actions,” then “Manual actions.”
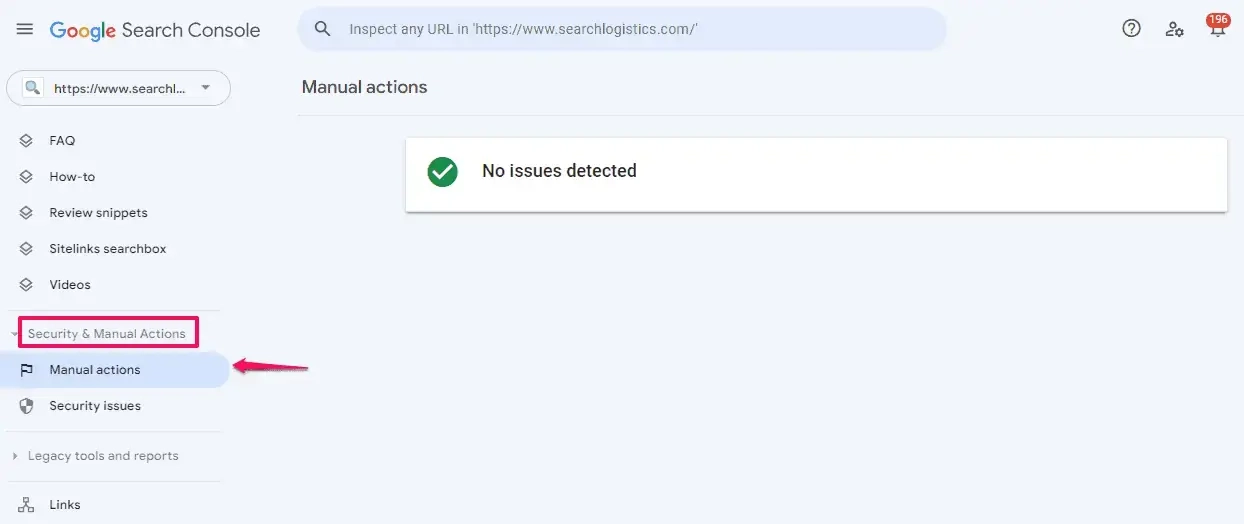
If there is a manual action listed, click on the 'Request Review' button:
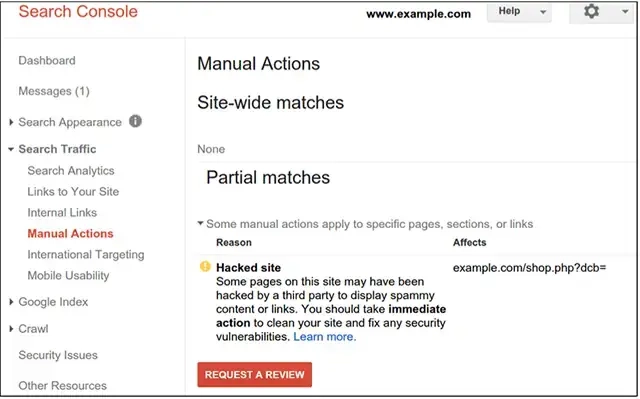
Provide a detailed description of the actions you have taken to resolve the issues. This should include examples of links you’ve removed or disavowed, and any other steps taken to comply with Google's guidelines.
Finally, submit your reconsideration request. Once you've submitted your request, you'll receive a confirmation message in the Message Center confirming receipt. Wait for a response from Google confirming whether or not they will reconsider the penalty.
How to prevent an unnatural links penalty
If you haven’t been issued a manual action against your website yet, you may be wondering what you can do to prevent getting penalized in the first place.
Here are our top tips:

Review your backlink profile
Reviewing your backlink profile should always be part of your link-building strategy, even if you haven’t received a penalty.
You can do this by conducting an audit—for example, with the Semrush backlink audit tool discussed earlier on.
You should run this kind of audit at least once every 3 months and monitor your backlink profile for any number of suspicious inbound links.
Vary your anchors
Spend time evaluating your anchor text and editing them where necessary. The best route to take is to vary your anchors and use similar or related keywords.
If you’re ever in doubt as to what you should do about an unnatural link in your backlink profile, it’s best to go the nofollow route.
Disavow spam
If you detect spam in your backlink profile audit, remove or disavow those links as quickly as possible.
As explained above, dealing with a Google penalty is a tricky and extensive process. It can also lead to significant revenue loss if your website and marketing strategy rely on organic search traffic.
As such, prevention really is key when it comes to unnatural backlinks. You can ensure you avoid unnatural link penalties by running consistent audits and keeping your profile clean.
How to Build Links More Naturally
To build links more naturally, avoid practices such as buying links, participating in link schemes, or excessively exchanging links with other websites.
If you engage in any of the above, Google and other search engines are likely to flag your website. This is because search engines scrutinize backlinks for repetitive or unusual patterns, such as:
PBNs (Private Blog Networks)
Low-quality directories
Spammy blog comments
Avoid unnatural link patterns
If you want to check whether your backlink profile contains patterns of unnatural links, you can use the Semrush Backlink Audit tool to spot them.
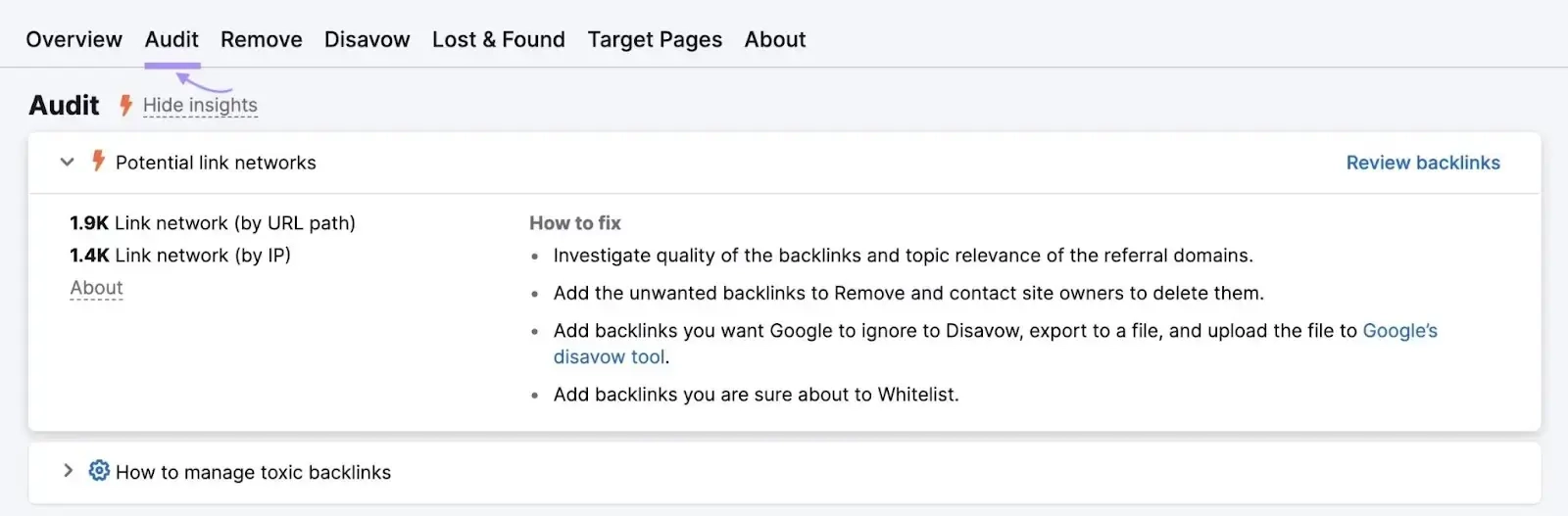
Here, you’ll be able to see the anchor, authority score (AS), and toxicity score (TS) for each link:
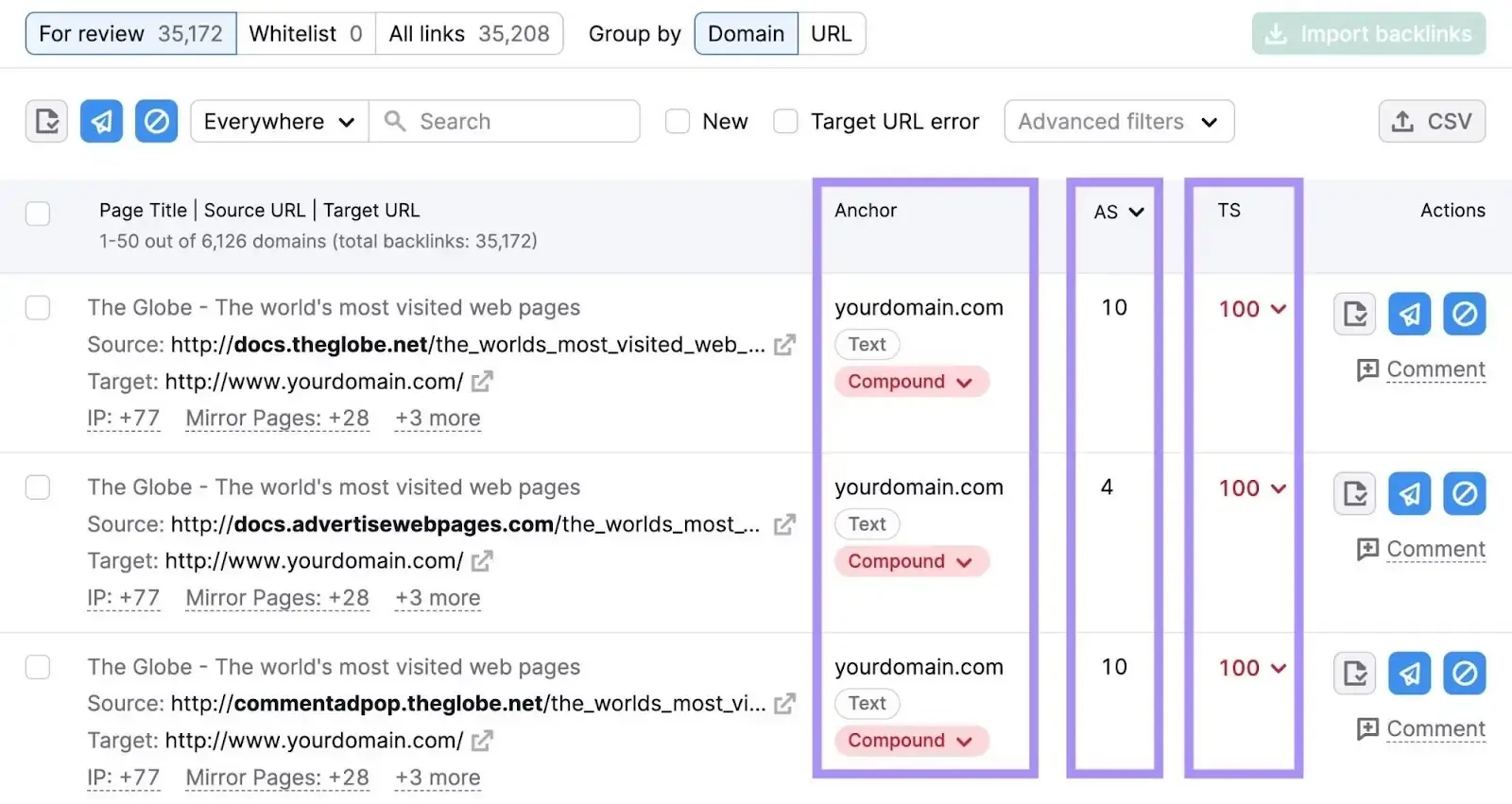
Hover over “TS” to see the toxic markers for each link. Semrush uses over 45 criteria to calculate the toxicity score. If more than 10% of your backlinks are toxic, your score will be high.
From here, you can categorize backlinks into:
Whitelist
Remove
Disavow
Target relevant sources
Before you can build natural links, you need to have an in-depth understanding of your niche and target audience. What key topics are they interested in? Where do they spend their time online?
By pinpointing these details, you can target websites that align with your content and audience.
Once you know who your target audience is and what they’re interested in, you can begin honing in on relevant sources, such as:
Influencers and bloggers: Collaborate with thought leaders on guest posts, interviews, or product reviews. Their audience and credibility can drive quality traffic to your site, and you’ll also earn valuable natural backlinks.
Resource pages: Resource pages compile useful links on specific topics and are excellent targets for natural link-building. Identify resource pages related to your industry and pitch your high-quality content as a valuable addition.
Online communities: Participating in forums, Q&A sites, and social media groups relevant to your industry can help you build natural links and establish your authority within these communities.
Make your anchor text contextually relevant
Anchor text refers to the clickable words in a link that take you to another webpage.
Contextually relevant anchor text means that these clickable words directly relate to the content of the page you are linking to and make sense within the sentence they are placed in.
For example, if you have a link to a page that provides dog training tips, good anchor text would be "dog training tips" rather than just "click here."
Search engines like Google use anchor text to figure out what the linked page is about. When the anchor text is relevant, it helps Google’s crawlers understand the structure and content of your website—which makes it easier for them to index and rank your site in the Google search results.
Wrapping Up on Unnatural Links
The last thing you want as a link builder is to receive a Google penalty for unnatural links. This can undo the link-building strategy you’ve worked so hard to implement. It also means spending valuable hours trying to have Google lift a manual action issued against your website.
One of the best ways to ensure you avoid unnatural links in your website’s backlink profile is to have a professional and reputable agency handle your link building for you. This way, you have trained link-building specialists on board who understand how to build valuable and contextual links, and who will help you avoid harmful and toxic links appearing in your backlink profile.


